Pioneering (Scouting)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In the Scout Movement, pioneering is the art of using ropes and wooden spars joined by lashings and knots
to create a structure. Pioneering can be used for constructing small
items such as camp gadgets up to larger structures such as bridges and
towers. These may be recreational, decorative, or functional.[1][2]Pioneering is used to teach practical skills, teamwork and problem solving. It is widely used in Scouting and Girl Guiding. Many Scout and Guide groups train their members in pioneering skills and construct projects, both small and large. In camp, Scouts may construct functional items like tables, camp dressers and gadgets, as well as decorative camp gateways. Pioneering is a common merit badge in many countries, and was required for the Eagle Scout rank in the 1920s and 1930s.
The name comes from the 18th and 19th century military engineers who went ahead of an army to "pioneer" a route, which could involve building bridges and towers with rope and timber (for example the Royal Pioneer Corps).
Pioneering skills include Knot tying (tying ropes together), lashing (tying spars together with rope), whipping (binding the end of a rope with thin twine), splicing (joining or binding the end of a rope using its own fibres), and skills related to the use, care and storage of ropes, spars and related pioneering equipment.
Contents |
Basic knots

A monkey bridge under construction
There are also a number of specialized pioneering knots that are used to add safety and functionality to pioneering projects:[4]
Basic lashings
- Square lashing, used to join two poles mostly at right angles
- Diagonal lashing, used when securing two spars when they need to be sprung together as in the 'X' of an H-frame trestle
- Round lashing, used to join two poles in a straight line
- Sheer lashing, used to join two poles in a scissors shape
Pioneering structures
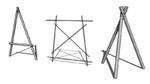
These basic structures are the building blocks for a number of pioneering projects:- A-Frame - The basis of many tower structures. The horizontal member of the A-frame also makes a convenient springing point for a deck such as a table-top.
- Trestle - Used as a modular element for building bridges and towers. Also used as a 'chariot' for inter-Patrol chariot races. Often referred to as X-Trestle or H-Trestle
- Tripod - As end supports for swingbridges, dining tables, etc. and as the basis for the hourglass tower. A tripod is not considered secure unless its legs are staked or otherwise attached to the ground.
Pioneering projects

A ferris wheel constructed by Swedish Scouts
- Camp gateways
- Chippewa Kitchens
- Bridges
- Dressers
- Tables
- Camp gadgets
- Chairs
- Benches
- Flagpoles
- Towers
- Rafts
- Aerial runways
- Swinging Ships
- Merry-Go-Rounds
- Ferris Wheel
- Catapults
- Ballistas
- Trebuchets
- Swing Sets
- See Saws


Geen opmerkings nie:
Plaas 'n opmerking